Systematic Error Examples : How Important Is To Detect Systematic Error In Predictions And Understand Statistical Applicability Domain Of Qsar Models Sciencedirect

These may be due to inaccuracy in the . All experimental uncertainty is due to either random errors or systematic errors. Systematic error (also called systematic bias) is consistent, repeatable error associated with faulty equipment or a flawed experiment design. Systematic errors concem the possible biases that may be present in an observation. As i have the idea, the consistent error made by the learners can be defined as the systematic errors. Systematic errors will shift measurements from their true value by the same amount or fraction and in the same direction all the time. These may be due to inaccuracy in the . A common example is the zeroing of a measuring instrument such as a balance .
These may be due to inaccuracy in the . Understandings:experimental design and procedure usually lead to systematic errors in measurement, which cause a deviation in a particular . Systematic errors concem the possible biases that may be present in an observation. A common example is the zeroing of a measuring instrument such as a balance . "examples of large, unsuspected systematic errors are numerous . And that can be reduced. How to minimize experimental error: These do not affect the .

All experimental uncertainty is due to either random errors or systematic errors.
These may be due to inaccuracy in the . And that can be reduced. A common example is the zeroing of a measuring instrument such as a balance . How to minimize experimental error: Systematic errors will shift measurements from their true value by the same amount or fraction and in the same direction all the time. ○ this is a systematic mistake (bias) and not a systematic uncertainty! The ansi definition that a systematic error is not really an error at all; As i have the idea, the consistent error made by the learners can be defined as the systematic errors. Understandings:experimental design and procedure usually lead to systematic errors in measurement, which cause a deviation in a particular . Systematic errors concem the possible biases that may be present in an observation.
Systematic errors will shift measurements from their true value by the same amount or fraction and in the same direction all the time. These may be due to inaccuracy in the . Systematic errors concem the possible biases that may be present in an observation. All experimental uncertainty is due to either random errors or systematic errors. Systematic error (also called systematic bias) is consistent, repeatable error associated with faulty equipment or a flawed experiment design. "examples of large, unsuspected systematic errors are numerous . ○ this is a systematic mistake (bias) and not a systematic uncertainty! A common example is the zeroing of a measuring instrument such as a balance . As i have the idea, the consistent error made by the learners can be defined as the systematic errors. And that can be reduced.
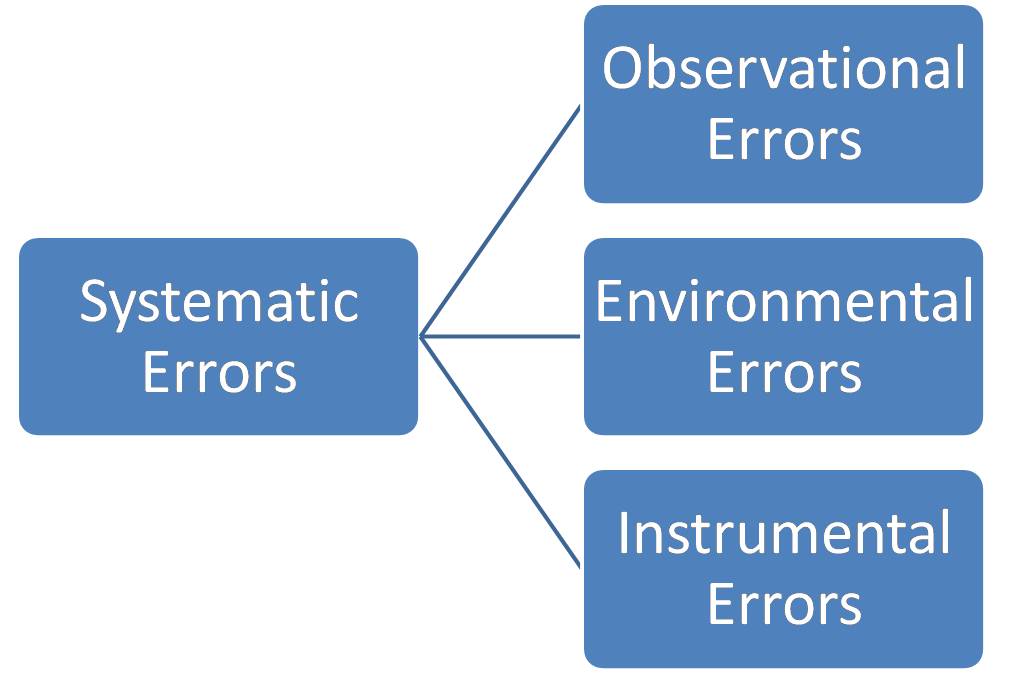
As i have the idea, the consistent error made by the learners can be defined as the systematic errors.
These may be due to inaccuracy in the . "examples of large, unsuspected systematic errors are numerous . These do not affect the . As i have the idea, the consistent error made by the learners can be defined as the systematic errors.
○ this is a systematic mistake (bias) and not a systematic uncertainty! As i have the idea, the consistent error made by the learners can be defined as the systematic errors. The ansi definition that a systematic error is not really an error at all; How to minimize experimental error: A common example is the zeroing of a measuring instrument such as a balance . All experimental uncertainty is due to either random errors or systematic errors.
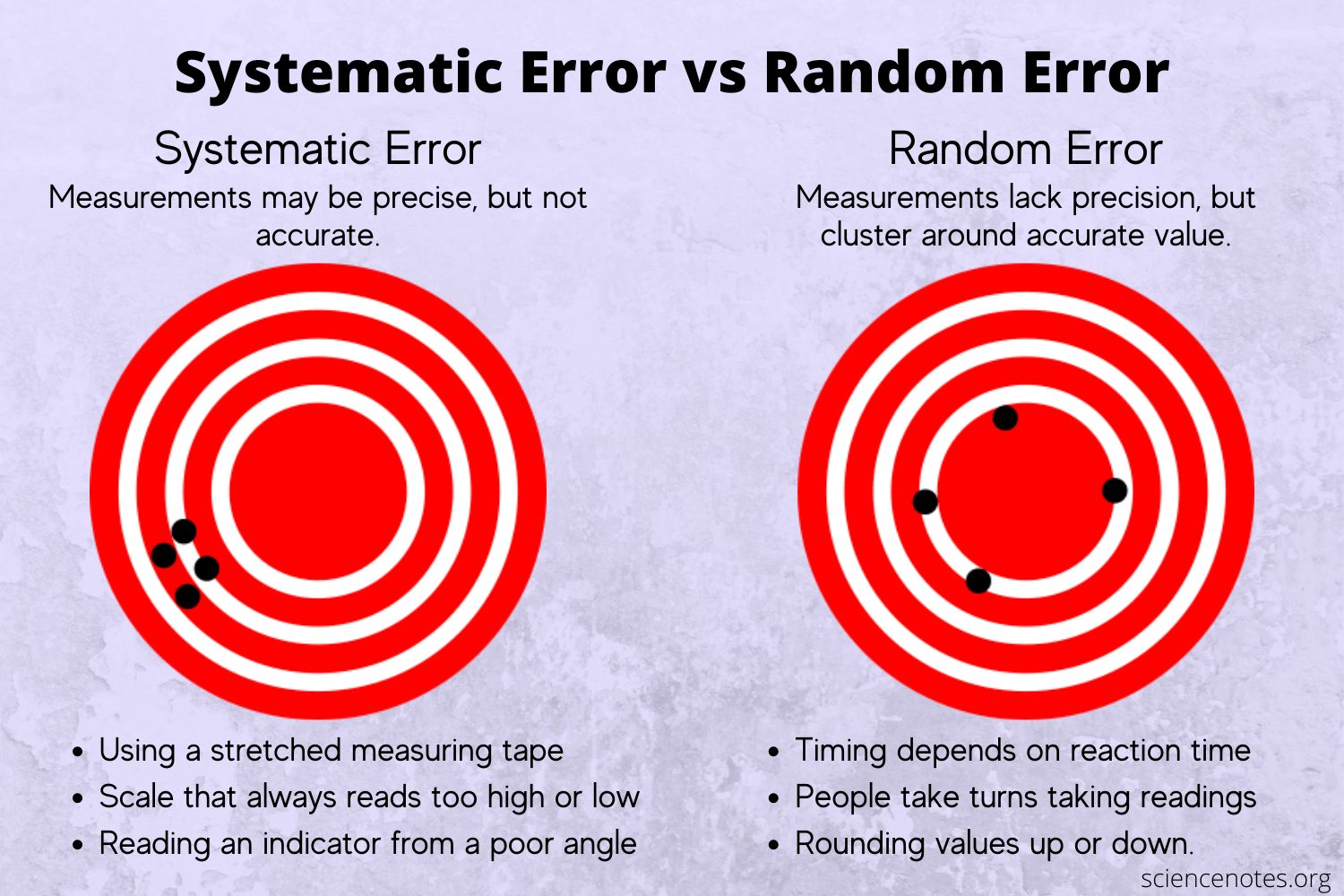
"examples of large, unsuspected systematic errors are numerous .
○ this is a systematic mistake (bias) and not a systematic uncertainty! And that can be reduced. Understandings:experimental design and procedure usually lead to systematic errors in measurement, which cause a deviation in a particular . Systematic error (also called systematic bias) is consistent, repeatable error associated with faulty equipment or a flawed experiment design. How to minimize experimental error: Systematic errors concem the possible biases that may be present in an observation. Systematic errors will shift measurements from their true value by the same amount or fraction and in the same direction all the time. These do not affect the . All experimental uncertainty is due to either random errors or systematic errors. A common example is the zeroing of a measuring instrument such as a balance .
Systematic Error Examples : How Important Is To Detect Systematic Error In Predictions And Understand Statistical Applicability Domain Of Qsar Models Sciencedirect. A common example is the zeroing of a measuring instrument such as a balance . And that can be reduced. Systematic errors will shift measurements from their true value by the same amount or fraction and in the same direction all the time. ○ this is a systematic mistake (bias) and not a systematic uncertainty!
These do not affect the systematic error. "examples of large, unsuspected systematic errors are numerous .